Breed Standard
BREED STANDARD FOR THE ROTTWEILER BRIEF HISTORICAL SUMMARY - The Rottweiler is considered to be one of the oldest breeds of dog. Its origin goes back to Roman times. These dogs were kept as herder or driving dogs. They marched over the Alps with the Roman legions, protecting the humans and driving their cattle. In the region of Rottweil, these dogs met and mixed with the native dogs in a natural crossing.
|
Group: |
Group 6 (Utility) |
|
History: |
|
|
General Appearance: |
The Rottweiler is a medium to large size, stalwart dog, neither heavy nor light and neither leggy or weedy. His correctly proportioned, compact and powerful build leads to the conclusion of great strength, agility and endurance. |
|
Characteristics: |
Rottweiler breeders aim at a dog of abundant strength, black coated with clearly defined rich tan markings, whose powerful appearance does not lack nobility and which is exceptionally well suited to being a Companion, Service and Working dog. |
|
Temperament: |
Behaviour and character. Being good natured, placid in basic disposition and fond of children, he is very devoted, obedient, biddable and eager to work. His appearance is natural and rustic, his behaviour self assured, steady and fearless. He reacts to his surroundings with great alertness. |
|
Head And Skull: |
Cranial Region: |
|
Eyes: |
Of medium size, almond shaped, dark brown in colour. Eyelids close fitting. |
|
Ears: |
Medium size, pendant, triangular, wide apart, set on high. With the ears laid forward close to the head, the skull appears to be broadened. |
|
Mouth: |
Teeth strong, complete dentition (42 teeth) with scissor bite, the upper incisors closely overlapping the lower incisors. |
|
Neck: |
Strong, of fair length, well muscled, slightly arched, clean, free from throatiness, without dewlap. |
|
Forequarters: |
Seen from the front, the front legs are straight and not placed too closely to each other. The forearm seen from the side, stands straight and vertical. The slope of the shoulder blade is about 45 degrees to the horizontal. |
|
Body: |
Back: Straight, strong, firm. |
|
Hindquarters: |
Seen from behind, legs straight and not too close together. When standing free, obtuse angles are formed between the dog’s upper thigh and the hip bone, the upper thigh and the lower thigh and the lower thigh and the rear pastern (metartasal). |
|
Feet: |
Front: Round, tight and well arched; pads hard, nails short, black and strong. |
|
Tail: |
Docked: Docked at the first or second joint. Level in extension of the upper line (topline). At ease may be carried down. |
|
Gait/Movement: |
The Rottweiler is a trotting dog. In movement the back remains firm and relatively stable. Movement harmonious, steady, full of energy and unrestricted, with good stride. |
|
Coat: |
The coat consists of a top coat and an undercoat. The top coat is of medium length, coarse, dense and flat. The undercoat must not show through the top coat. The hair is a little longer on the hind legs. |
|
Colour: |
Black with clearly defined markings of a rich tan on the cheeks, muzzle, throat, chest and legs, as well as over both eyes and under the base of the tail. |
|
Sizes: |
Height at withers for males is 61-68 cm (24-26 * ins) |
|
Faults: |
Any departure from the foregoing points should be considered a fault and the seriousness with which the fault should be regarded should be in exact proportion to its degree and its effect upon the health and welfare of the dog. |
|
Notes: |
Male animals should have two apparently normal testicles fully descended into the scrotum. |
Picture added to show acceptable tail carriage and also incorrect tail carriage
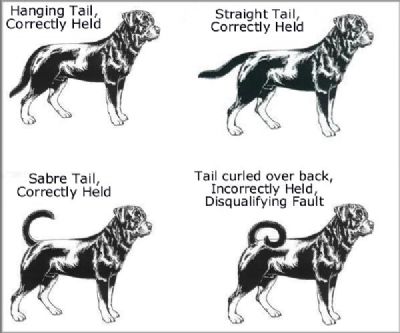
As taken from the ANKC website.
